
European consumers are concerned that faster drug development processes being pushed by regulators can be unsafe for patients. With the EMA spearheading discussion on medicines adaptive pathways to patients, or MAPPs, more convincing is needed.

European consumers are concerned that faster drug development processes being pushed by regulators can be unsafe for patients. With the EMA spearheading discussion on medicines adaptive pathways to patients, or MAPPs, more convincing is needed.
Successful project management requires efficiency in both identifying and addressing bottlenecks before they impact study timelines. This article examines how to design data collection criteria for optimal performance.

Peter O’Donnell writes that Brexit or or no Brexit, it will be interesting to see how far the industry rules are complied with across Europe now that the EFPIA disclosure code is also in force.

The UK's EU departure threatens to damage the foundation of several European-wide drug safety and innovation initiatives, and also leaves recent boasts from officials on things like partnership, networking, and transparency just empty words.

This 3-part series provides insight into ensuring compliance with the ICH E6 (R2) Addendum to take effect later this year. Part 3 covers the value of embracing a centralized, technology driven approach to risk based monitoring.

Today’s convergence of health data and technology is fun to watch unfold, but a focused vision on system and process integration-and the framework for continuous enrichment-will be key to future lasting gains for clinical research.

An updated release to the ICH E14 Guidance could indicate that data be used to replace a TQT trial for regulatory submission and review. The result of such a change would be a reduction in development time and costs for biopharma companies.

Using eClinical technologies to access vendor performance allows for researchers to choose appropriate vendors based on trial design, needs and risks. These decisions can be made using historical comparative data from a normative database.

A recent survey found that sponsors do not have the required metrics to properly assess their operational activities related to drug safety reporting. Applying capture technology is one way to better measure these processes and ensure consistent data quality for medical evaluation.

This 3-part series provides insight into ensuring compliance with the ICH E6 (R2) Addendum to take effect later this year. Part 2 covers steps that organizations can take today to begin adopting a centralized technology-based approach to risk management.

Patient recruitment remains a challenge for both the biopharma industry and the oncology research community. New recruiting platforms in development have the potential to change the way the industry uses technology, data and the internet to augment recruiting efforts.

This 3-part series provides insight into ensuring compliance with the ICH E6 (R2) Addendum to take effect later this year. Part 1 covers the addendums implications, objectives, requirements and advantages.

Faced with new EMA guidance on anonymizing clinical trial data, drug manufacturers have two choices – do what it takes to meet the November deadline and prioritize clinical study reports, or embrace a more sustainable strategy that starts with the patient-level data.

Renewed attention on ways to tackle this age-old scourge is building in Europe and beyond.

Many have inquired about writing an RBM plan due to recent changes in industry execution and an increase in RBM experiences. Moe Alsumidaie responds with a brief methodology on developing a risk management process to create an RBM plan.

Analysis from multiple reports shows that Phase I clinical trials typically have a low rate of success. The lowest success rate occurs during Phase II of research, while those who make it to Phase III do not fare much better.

Identity trust platforms assure clinical investigators that their credentials are legitimate by allowing use of a single identity that can be recognized across multiple entities. These platforms support collaboration by allowing drug development participants to access data, sign and exchange documents.

Regardless of whether the UK does decide to leave the EU or not, the concern over medication will remain for the rest of Europe. The needs of these countries will persist at a human and public health level for more effective medicines and more effective ways of paying for them.

Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a common neurodevelopmental disorder which does not have an approved medication to address its core symptoms. The Janssen Autism Knowledge Engine (JAKE) was designed to advance the clinical research process for autism by integrating emerging technologies into traditional clinical trial processes.
![CyndiVerst[1].png](https://cdn.sanity.io/images/0vv8moc6/act/460bbdd742506542c78e095aa023319ebc3cd470-250x250.png?w=350&fit=crop&auto=format)
Clinical trials of the future may be closer than we think as we strive to deliver smarter, faster and more cost effective treatment to patients. The data exists to make this possible, now we must change our thought process to meet the needs of patients and sponsors.

Peter O'Donnell writes that the EMA surprisingly diverted from it's usually strict boundaries on it's annual report published in May.

Pfizer has created a clinical trial modeling tool for mitigating study risk during the protocol design and study execution phases. Jonathan Rowe speaks with Moe Alsumidaie on the purpose behind these predictive models.

A risk-based approach to quality trial oversight, adopted by the FDA and EMA, has resulted in an array of new technology solutions being released.

The early implementation of post authorization safety studies (PASS) will translate to efficiencies in pre-appoval research. These benefits allow for faster approval and wider patient access to potentially life saving therapies.
![Wayne Kubick photo[1].jpg](https://cdn.sanity.io/images/0vv8moc6/act/937ea3115e353ce57e83109baff0c323df1e0723-253x352.jpg?w=350&fit=crop&auto=format)
FHIR (pronounced "fire") is a new, free of cost, platform that has the ability to access and create data though EHR systems. Wayne Kubick writes that using such a platform could truly re-engineer how pharma collects data during clinical trials.

Sponsors and their contractors have faced challenges when ensuring that parties involved in global clinical trials adhere to rules and regulations regarding biomedical research. For an effective collaboration to take place, all parties must meet the expectations and accountabilities detailed in the trial contract.

The Innovative Medicines Initiative, a drug research program run by the European Commission and the EFPIA, is inviting bids to run a pilot program regarding preclinical research and development.
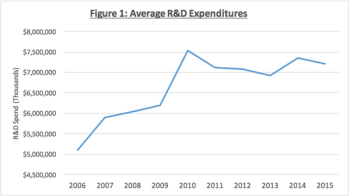
Some in the financial industry have argued that we may be in the midst of another economic recession. The biopharmaceutical industry has shown resiliency during such times and industry trends point to that being the case again.

The Movement Disorders Society has recently published Clinical Diagnostic Criteria for Parkinson’s disease. These new guidelines allow for the diagnosis of clinically established and clinical probable Parkinson’s disease, which will help reduce errors in clinical trials.

With Britain’s potential succession from the EU looming, scientific leaders in Europe are voicing their concerns that losing the UK would be a blow to clinical research.