
FDA encourages clinical data e-submission and boosting development of new therapies to combat bioterrorism, cancer, and obesity.

FDA encourages clinical data e-submission and boosting development of new therapies to combat bioterrorism, cancer, and obesity.

New standards and research methods aim to provide more useful information on population subgroups.

FDA and NIH investigate staff relationships with industry to eliminate any outside influence on regulatory decisions and clinical trial procedures.

Federal agencies seek to curb redundant IRB procedures and encourage voluntary accreditation of research organizations.

New technologies and research methods aim to reduce study failures and spur drug development.

McClellan shifts to head Medicare after delivering new proposals to block counterfeits, add bar codes, and assess drug imports.

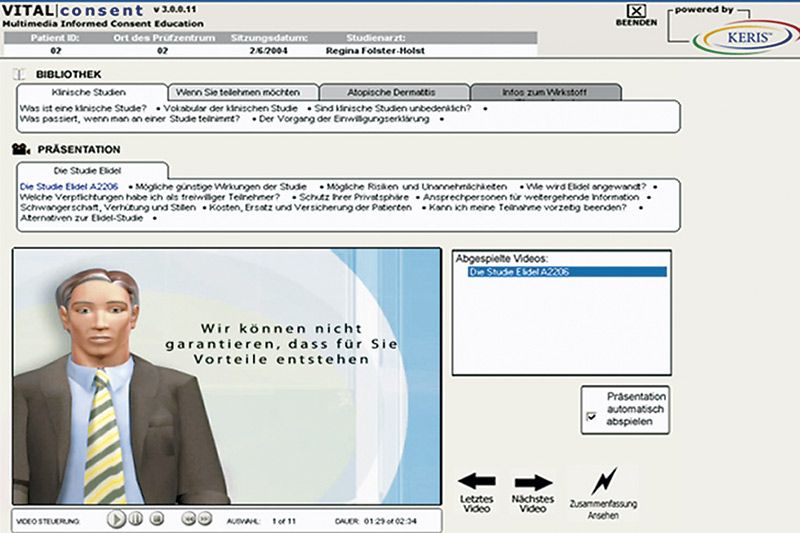
Although the worlds of EMR and clinical trial technologies are similar, they have quite a few differences as well.

Policymakers want to harmonize for safety reporting, IRB operations, patient access, and other areas to spur product development.

Starting points for meeting eSource data regulatory requirements

FDA eyes e-data submissions to improve regulatory oversight and ensure appropriate and safe drug use.

After a long, contentious battle, Republicans mustered up enough votes just before Thanksgiving to approve a massive, complex bill designed to overhaul Medicare policies and provide coverage for prescription drugs.

This past year has been one of tremendous activity at the Food and Drug Administration, and at other government agencies involved with healthcare, biomedical research, and national security.

New initiatives would form networks and harmonize standards to translate basic research into needed treatments.

FDA plans to rewrite rules governing electronic records while offering new policies to encourage risk-based regulatory approaches to application review and inspections.

FDA is exploring policies to incorporate genomic information into the regulatory process.

HHS offers IRBs, institutions, and investigators points to consider when dealing with financial relationships and conflicts of interest in clinical research.

FDA is revising its policies that govern electronic recordkeeping, clarifying standards for measuring subject outcomes, and seeking to encourage pediatric studies.

The HIPAA privacy policy limits the use of protected health information to that required or permitted by regulations.

Sponsors tackle international research challenges to develop AIDS, malaria, and TB therapies for developing nations.

Congressional efforts to establish a Medicare pharmacy benefit will affect R&D, and a new FDA commissioner promises change.

Federal agencies seek to enhance IRB operations as new policies further expand board responsibilities.

Although a Medicare drug benefit appears unattainable this year, Congress is considering other measures to reduce the cost of medicines.

PDUFA III boosts manufacturer fees to expand postapproval surveillance and support new FDA review initiatives.

Sponsors are underwriting more studies of children, but controversy continues over the need for FDA?s pediatric rule and the impact of extended exclusivity on generics.

Rules to ensure confidentiality of individual health information threaten to make clinical trials more complex and costly.